

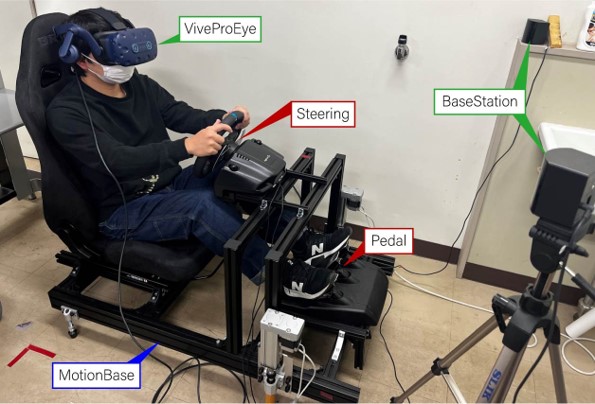
Driving simulator with eye-measurable HMD and VR environment
We are developing a driving ability test for the elderly and patients who are recovering from brain diseases.
The aim is to construct a quantitative evaluation index to support resumption of driving and return of driver's license.
A scenario in which pedestrians come out from the left and right while driving at approximately 60 km/h on a one-lane straight road was created. Driving ability is evaluated by analyzing the presence or absence of a collision with a pedestrian, gaze, time required for braking, head movement, and so on.


Bicycle Simulator
We have developed a bicycle driving simulator that combines VR technology, magnetic motion capture technology, and various sensors to present a distant view of a virtual traffic environment that matches the visibility of reality, allows the driver to see the road surface near his or her feet, and enables the driver to brake.
The simulator aims to identify risk factors common to traffic accidents while riding a bicycle.

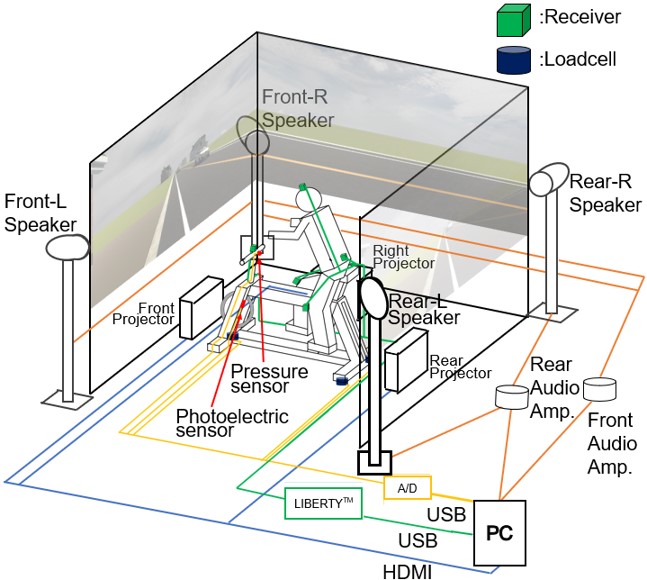

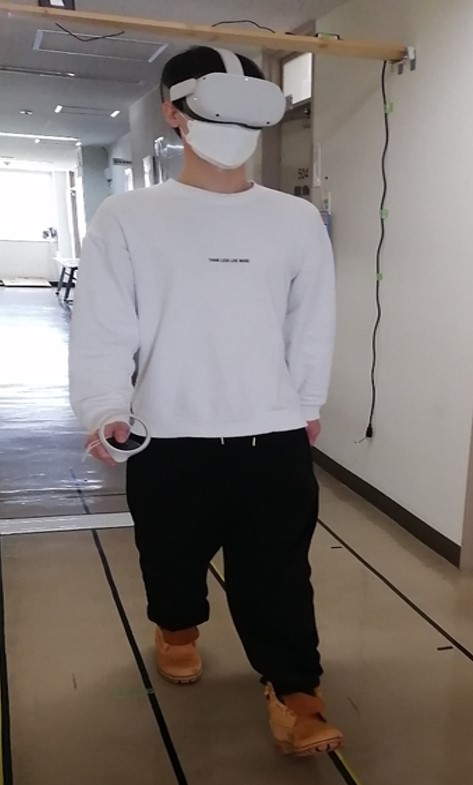
Walking Environment Simulator
In terms of the number of fatalities by traffic accident condition, the highest percentage of fatalities occurred while walking. Of these, 70% were killed while crossing the roadway. In order to prevent traffic accidents between pedestrians and vehicles, it is effective for pedestrians to learn safe crossing behaviors in addition to approaches to accident prevention from the driver's side.
This research aims to develop a "Wearable Walking Environment Simulator" that enables real-world walking in a virtual space using an HMD to simulate the hazards of crossing a roadway, and to measure pedestrian behavior in a virtual traffic environment to identify accident-prone pedestrian behavior.


Virtual Traffic Environment Inspection
Proposal of an audio guide production support method focusing on the volume balance with the movie
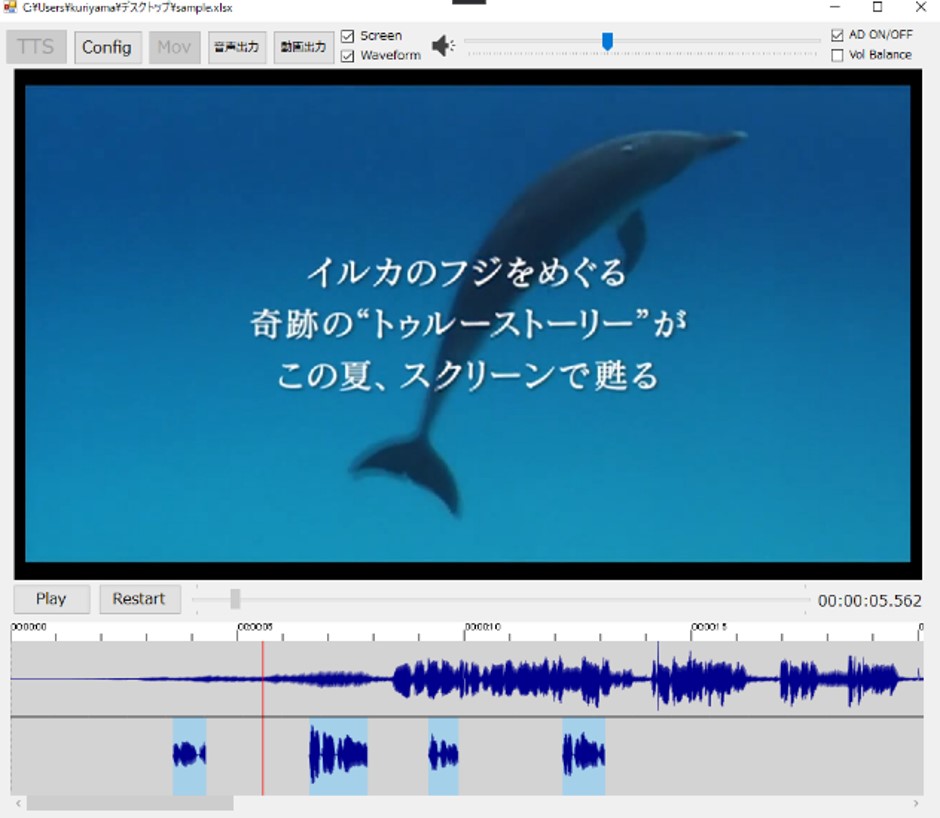
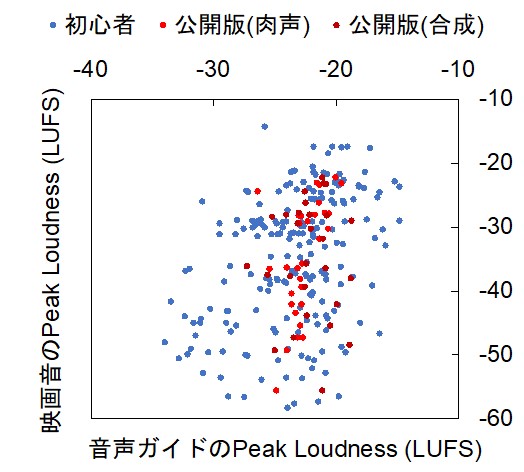
While many people enjoy watching movies, the visually impaired are not able to fully enjoy them due to the low popularity of audio-directed movie guides (ADs). We conducted an experiment using our voice guide production software (left figure) for beginners to produce an audio guide. Although the cost of production can be reduced by the participation of novices, the quality of the voice guidance system is degraded. We quantified the differences in volume settings between professionals and novices (right figure), and are studying ways to improve them.
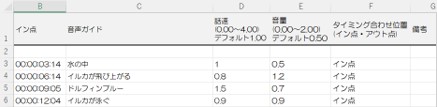
The Effect of Speech Speed of Movie Voice Guides on Listening and Impressions
In this study, we developed software that can adjust the speech speed of an audio guide by voice and keyboard operation in order to more actively reflect the opinions of the visually impaired in the production of the audio guide. Visually impaired people were asked to use the software to determine the optimal speech speed for both human voice and synthetic voice. In addition, young sighted people were asked to listen to the audio guide and rate it on a scale of 0 to 9 (Average score) for 10 questions. The results showed that the use of speech speeds selected by the visually impaired (synthetic speech SOO, speech HOO) significantly amplified the sense of presence and immersion, even for the original synthetic speech guide, which is inferior to the recorded version of the audio guide at the same speech speed.
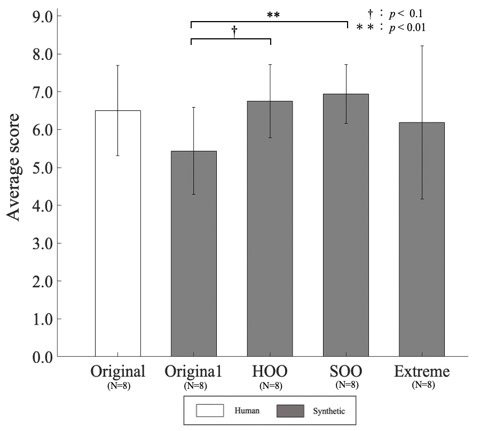
Research on non-fatiguing voice guidance focusing on voice quality of synthetic voice
Have you ever felt uncomfortable or unnatural when listening to a synthesized voice?
Currently, the quality of synthesized voices is such that it is difficult to tell the difference from a human voice when listening to short sentences. However, in situations where you listen to a synthetic voice for a long period of time, such as when listening to an audio guide for a movie, a slight discomfort or unnaturalness may lead to fatigue.
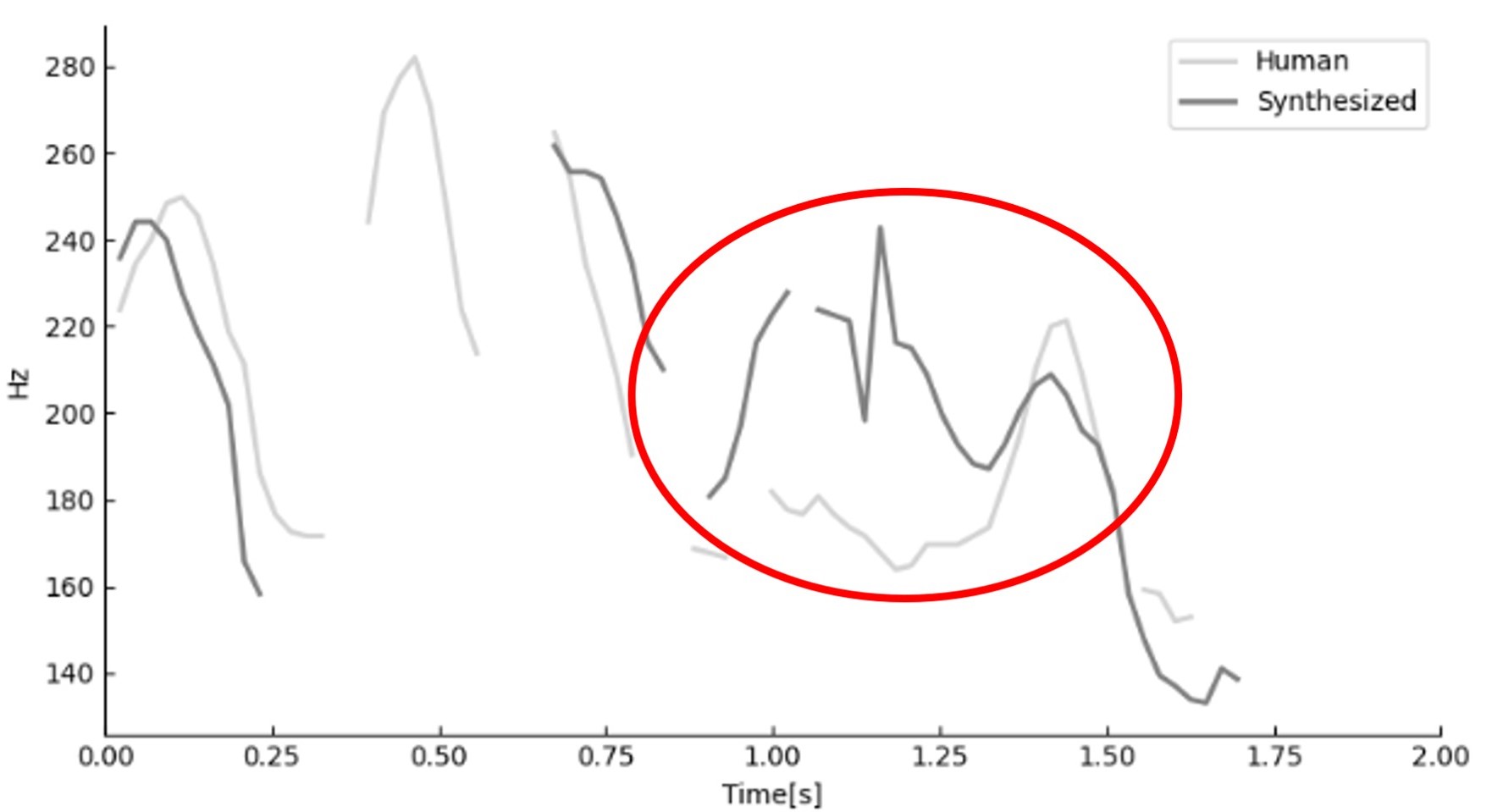
In this study, in order to improve the quality of voice guidance using synthetic voices, we evaluated "fatigue" and "ear fatigue" caused by movie voice guidance using both natural and synthetic voices, and investigated the causes. As a result, the discomfort and unnaturalness of three factors in particular, "intonation," "accent," and "pauses," were pointed out. The figure on the right shows a voice guidance system with different accents between a natural voice and a synthesized voice, using frequencies.
In the future, we plan to identify acoustic features corresponding to the three elements in order to create a natural voice guide.
Investigation of measurement methods in plant bioelectrical potentials to realize high quality countryside
Akita Prefecture aims to make its prefecture a "high-quality countryside" as a prefectural administrative policy starting in 2022. Therefore, the use of digital technology that takes advantage of the rich natural environment is required.
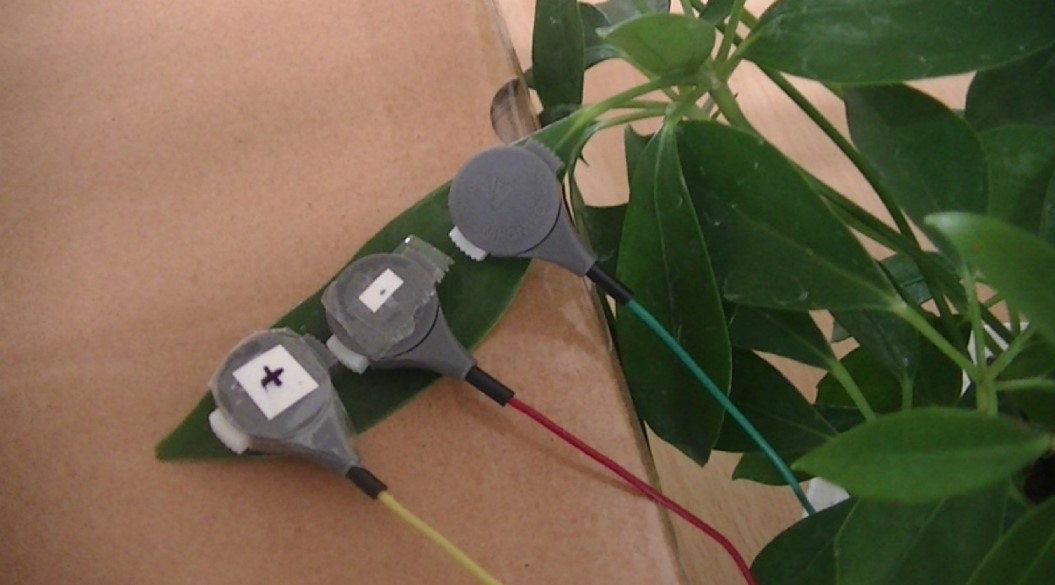
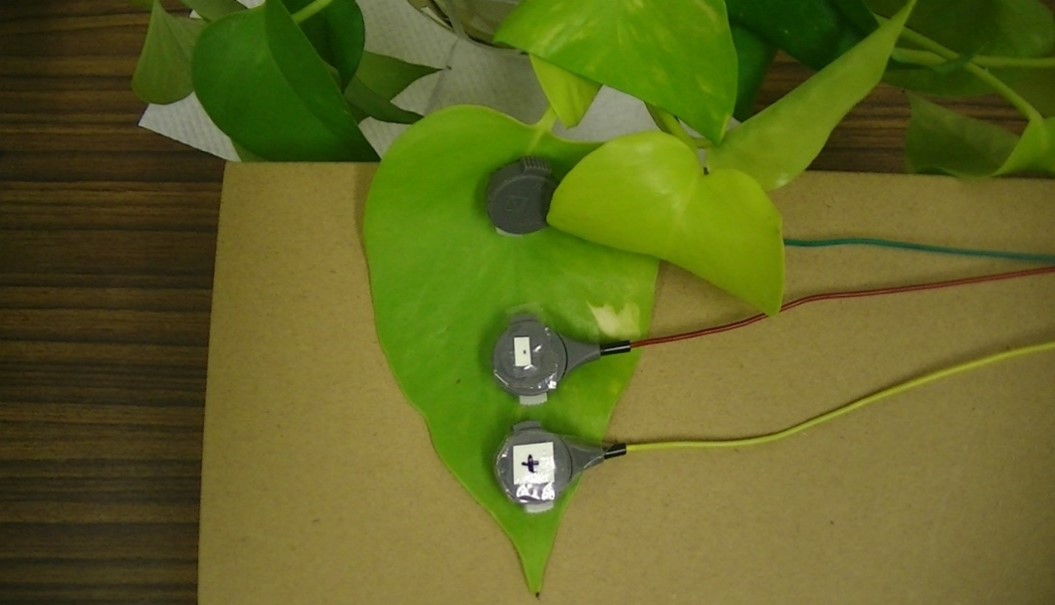
This study focuses on the bioelectric potential of plants, which changes depending on surrounding environmental factors, and aims to visualize the biological information of plants.
As shown in the figure, electrodes were placed on plant leaves and bioelectric potentials were measured under various conditions. The results showed that the bioelectrical potential was low at the beginning of the measurement and gradually increased to a stable value over time, but there were exceptions.
We plan to conduct additional experiments in the future for more detailed analysis.


Analysis of torso and lower knee forward tilt angle during chair standing up using an iPad equipped with a LiDAR scanner
An increasing number of elderly people are suffering from frailty, a condition in which their motor functions and other functions have deteriorated significantly and they will require nursing care in the near future.
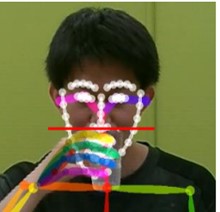
In this study, we aim to discover the factors that determine frailty by analyzing the anterior tilt angles of the trunk and lower knees related to the upper and lower body from the joint position coordinate data obtained by the standing up motion analysis application shown in Figure 1.
Cluster analysis, as shown in Figure 2, revealed a negative correlation between the trunk and lower knee forward tilt angles.
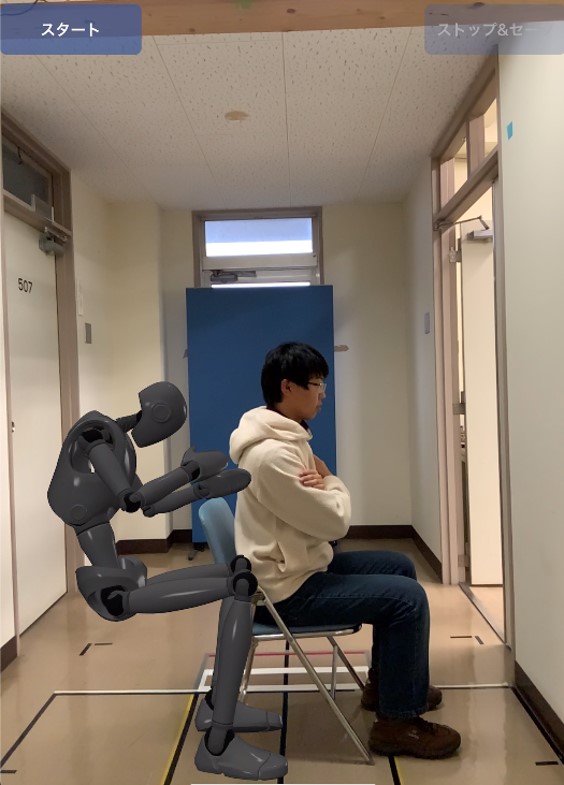

Fig.1 Example of a rising motion analysis application
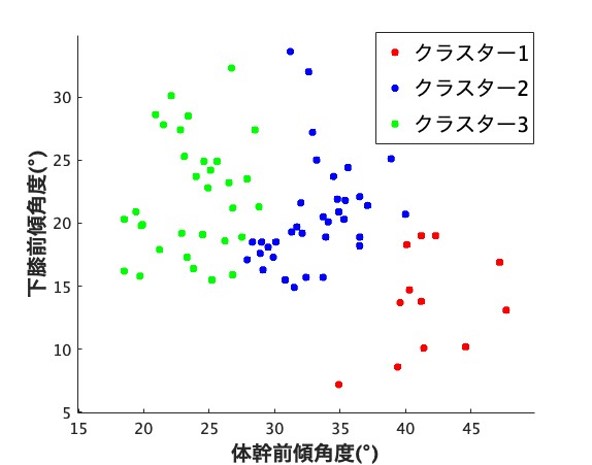
Fig. 2 An example of cluster analysis
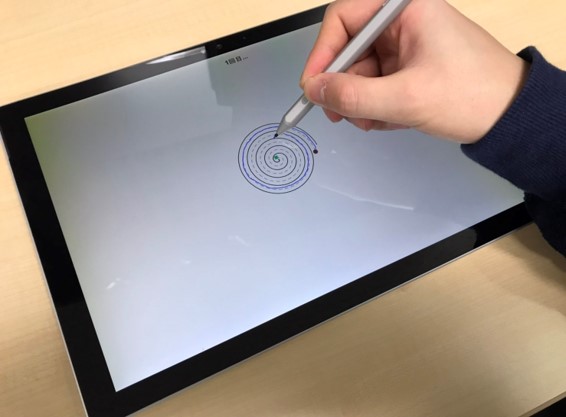
高齢者の認知機能評価のためのタブレット端末を用いた巧緻動作の解析
高齢者の軽度認知障害を早期発見するために,タブレット端末で渦巻きを描画する.これによって,得られた描画時間や渦巻きのずれなどを解析している.

Proposal of a Medication Action Analysis System Using OpenPose to Support Elderly People in Taking Medication
As the elderly population increases, the number of caregivers who care for the elderly and pharmacists who administer medications are decreasing year by year. As a result, the number of caregivers and pharmacists who can assist those who do not know which medicine to take by themselves is decreasing.
We are therefore developing an application called OpenPose, which visualizes the movements of elderly people as they take their medications, with the aim of helping them take their medications without assistance.
Development of an application for early detection of dementia using the iPhone
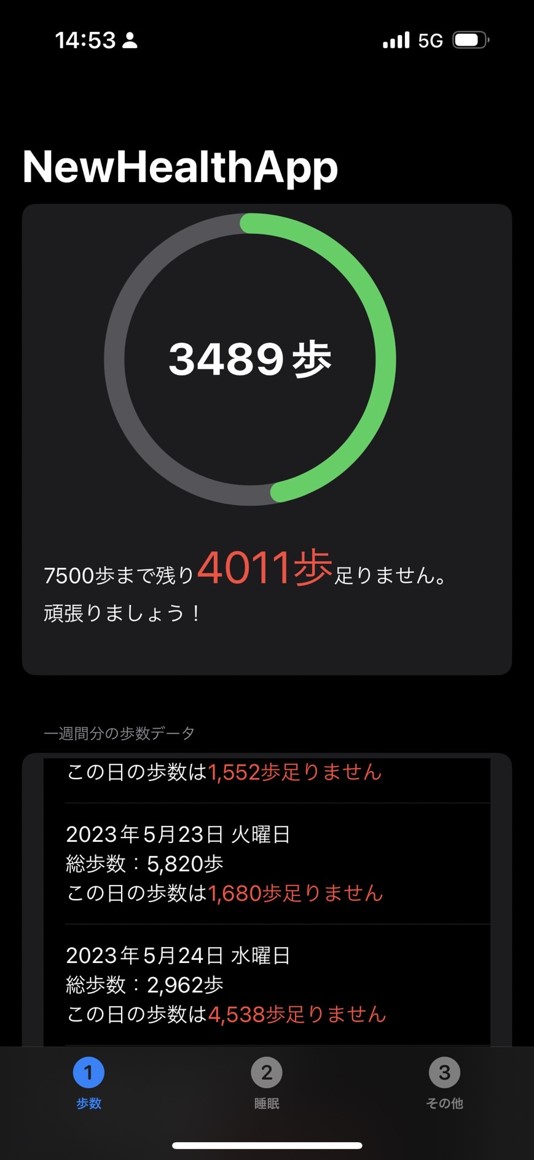
It has been confirmed that people who sleep less and take fewer steps per day are more likely to develop dementia. Therefore, we are developing an application that records the number of steps taken and the amount of sleep a day to detect dementia at an early stage.
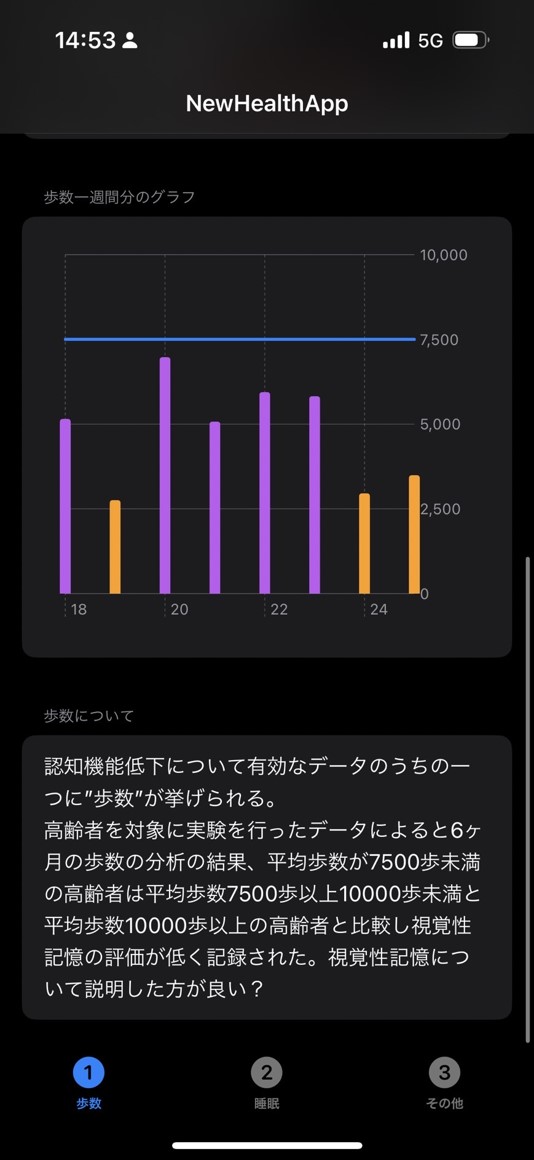
People who take less than 7,500 steps per day are more likely to develop dementia. Therefore, as shown in the image, the number of steps taken per day is compared with the 7500 steps taken per day, and it is displayed in an easy-to-understand manner to indicate how much is missing on a given day.
Development and evaluation of MR remote indication system for probe manipulation in ultrasonography
One form of telemedicine support is for a nurse to visit a patient's home and a physician to treat the patient remotely from a hospital. When ultrasonography is performed remotely, the physician gives verbal instructions to the nurse via videophone. However, the operation of the ultrasound probe in ultrasonography requires a high degree of expertise because the echo image produced differs depending on the position, angle, and strength of the probe. Therefore, it is difficult to give verbal instructions.
This study aims to develop a probe manipulation instruction system using mixed reality technology as an elemental technology for telemedicine, which enables nurses to perform ultrasound examinations while mimicking the movements of the ultrasound probe of a specialist doctor in a remote location.
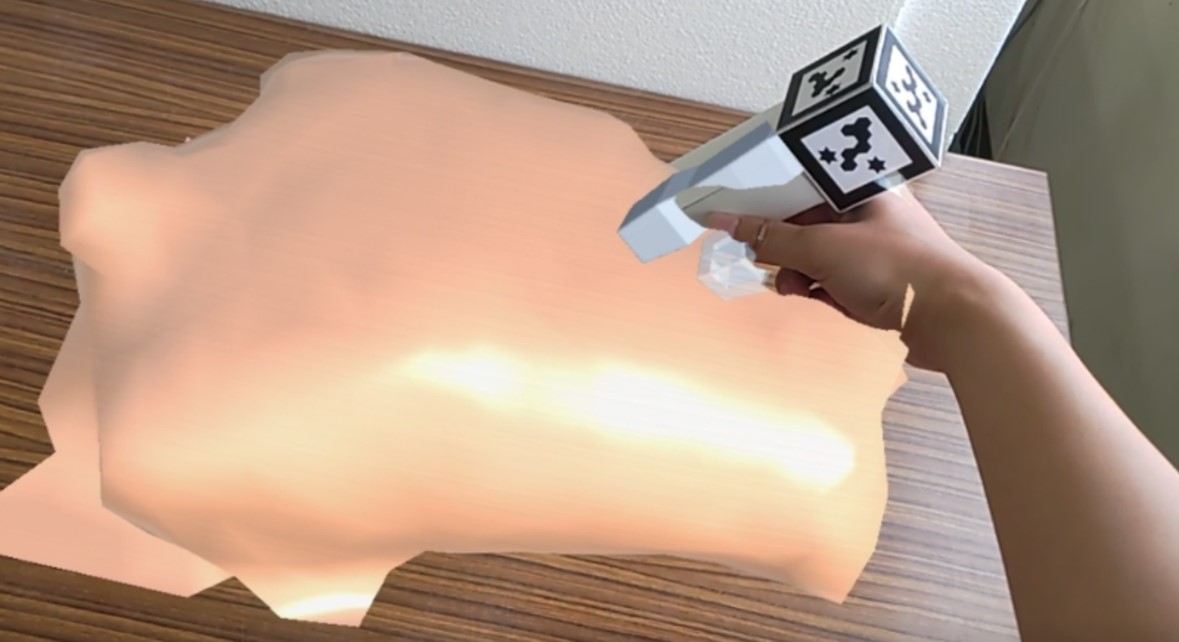


Evaluation of drawing function by finger on a board touched in VR space
Recently, education using VR technology is expected to improve learning motivation and learning efficiency. We have developed a tangibles-based handwriting input system that enables users to draw letters and figures in VR space while actually touching an acrylic board in real space. In general touch panels, a change in the capacitance between the built-in electrodes occurs when the user touches the panel, and the system judges whether the user has touched the panel or not. On the other hand, this system uses a magnetic motion capture device to measure the position and posture of the acrylic board and fingers in real space, and judges the contact between the fingers and the acrylic board to realize drawing characters and figures on the board in VR space.
In this study, we will conduct a comparison experiment by tracing Chinese characters on a real-space touch panel and a board in VR space, and evaluate the ease of writing the character input function of the system we have constructed.


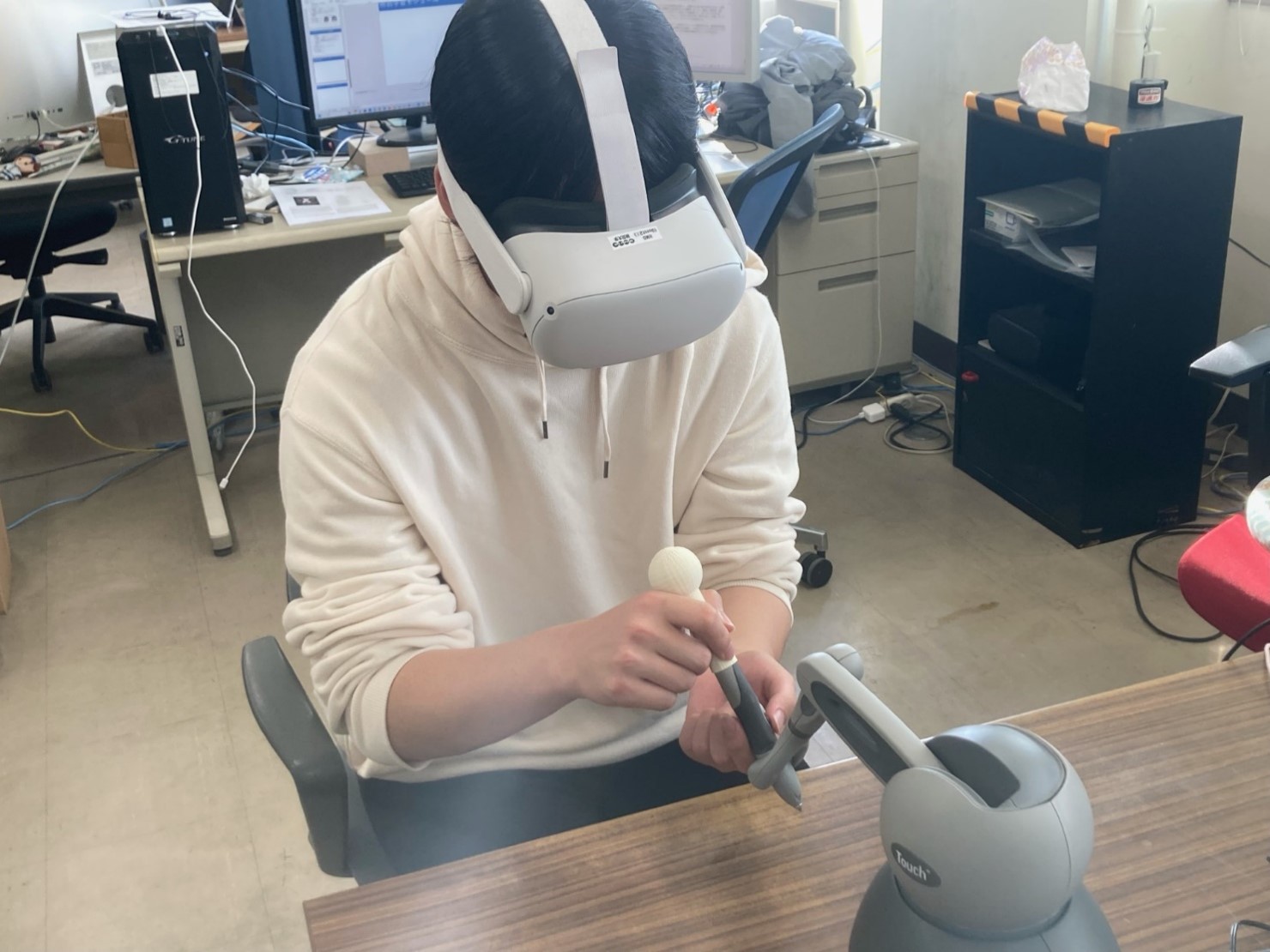
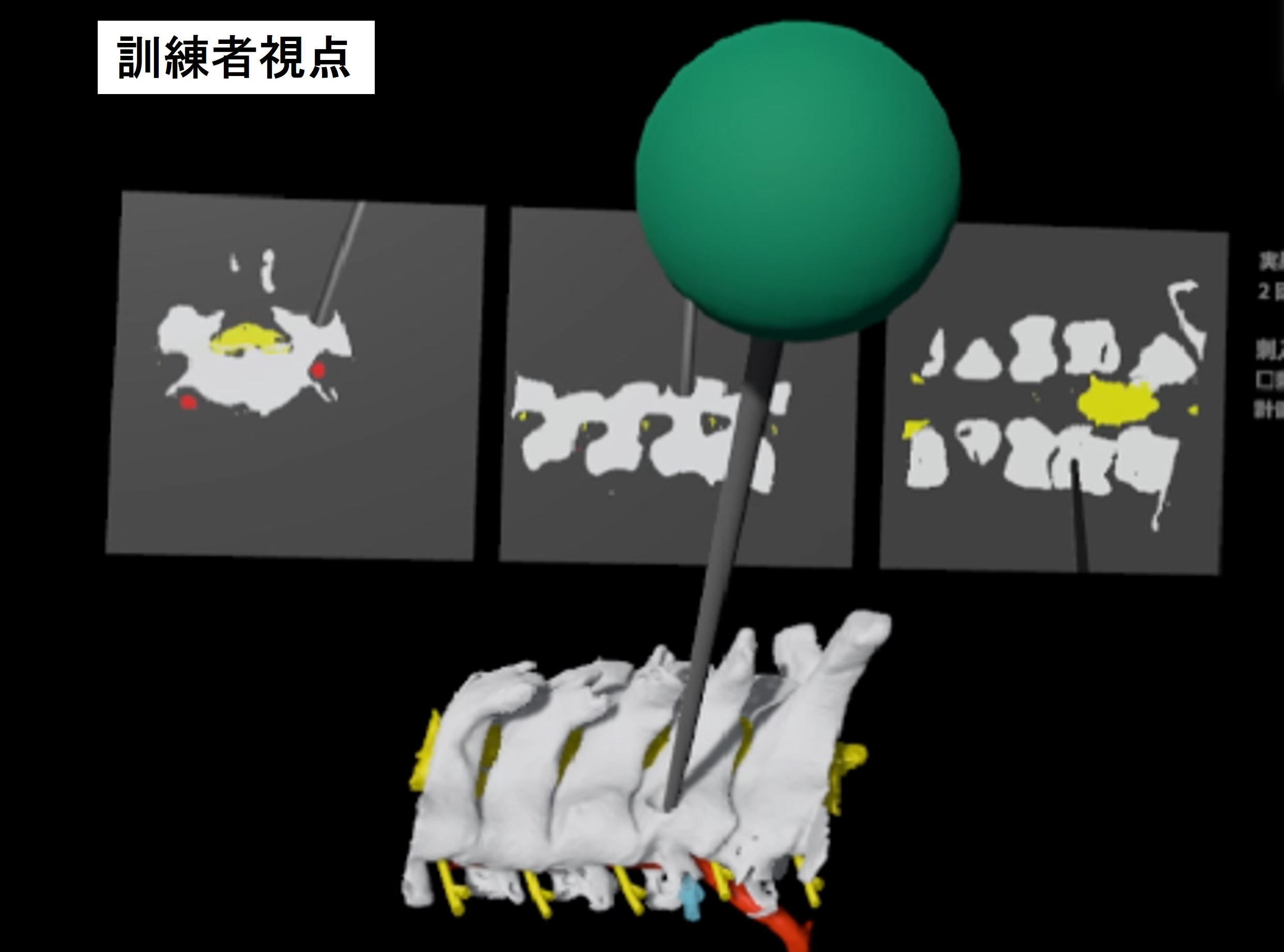
Development and Evaluation of a VR Training Simulator for Posterior Cervical Fusion
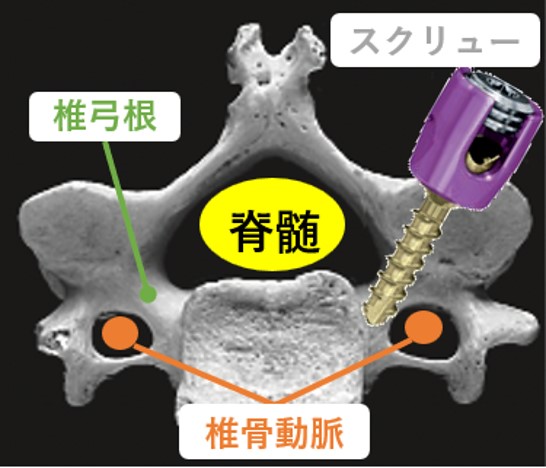
Posterior cervical fusion is a procedure in which screws are inserted into the vertebral arch root, which is a part of the spine, to fix the spine and correct deformities. However, because the vertebral arch root is thin and surrounded by many nerves such as arteries and spinal cord, care is required when inserting screws to avoid damage during surgery.
In this study, we utilize virtual reality (VR) to present visual information with depth using a head-mounted display (HMD) and tactile sensation of the bone using a force tactile device. We aim to develop a simulator that can train residents to repeatedly perform screw insertion and planning of the screw insertion route by creating an environment similar to that of a real surgery.

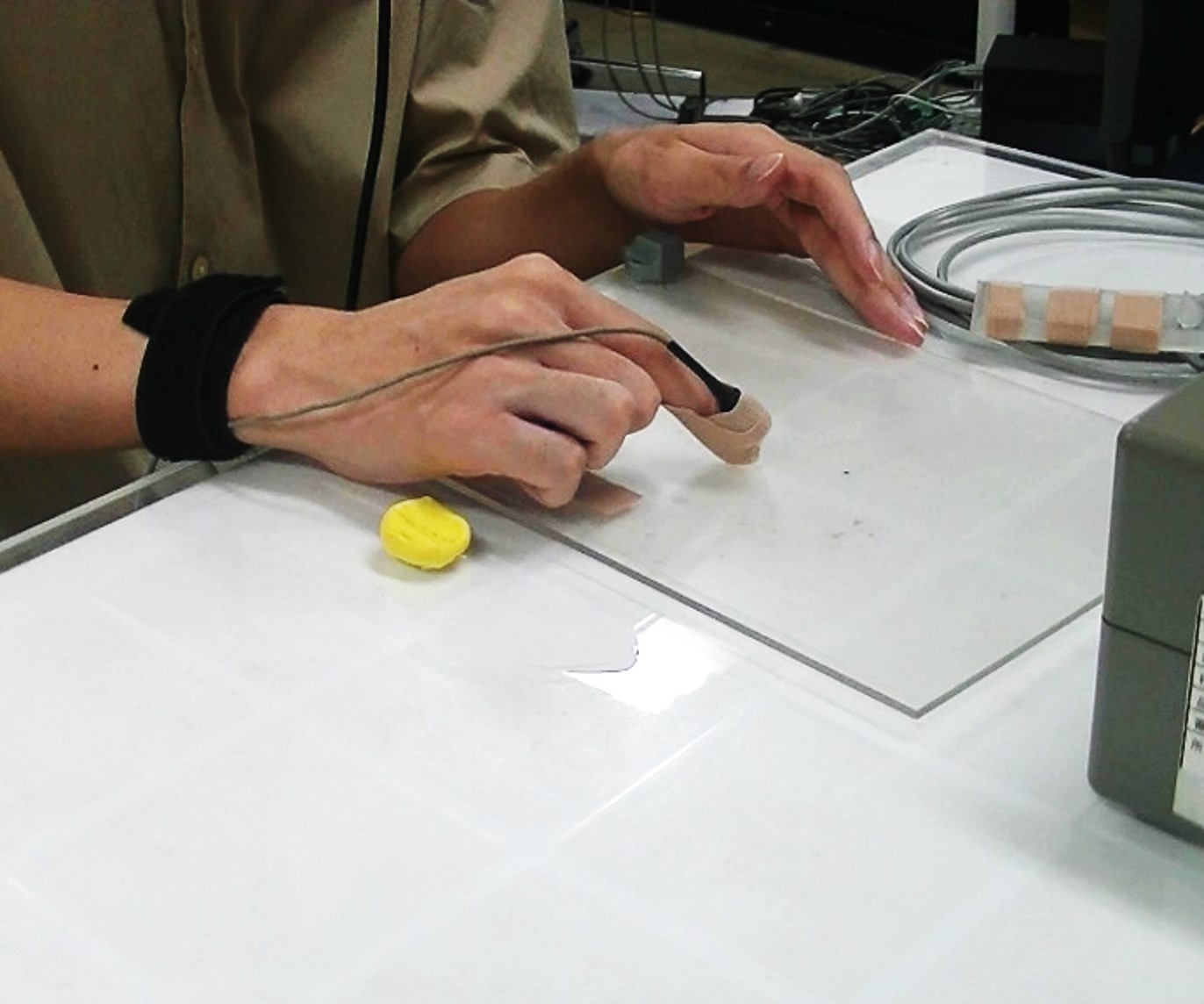
Devising and evaluating a visual presentation method for communicating the degree of force for skill transfer.
As the population continues to age and the birthrate declines, it is becoming increasingly difficult to secure skilled personnel in the small and medium-sized manufacturing industry every year. Skills accumulated over many years are the strength of small and medium-sized manufacturing industries, and a shortage of skilled personnel could jeopardize the survival of small and medium-sized manufacturing industries. As a solution to this problem, a learning method has been devised that aims to efficiently acquire skills by imitating and training preserved skilled skills using a VR space.
This study focuses on "force", which is difficult to observe in skill transfer, and develops a VR simulator for training that can easily and efficiently imitate force using visual and haptic feedback in a VR environment by using a haptic device.
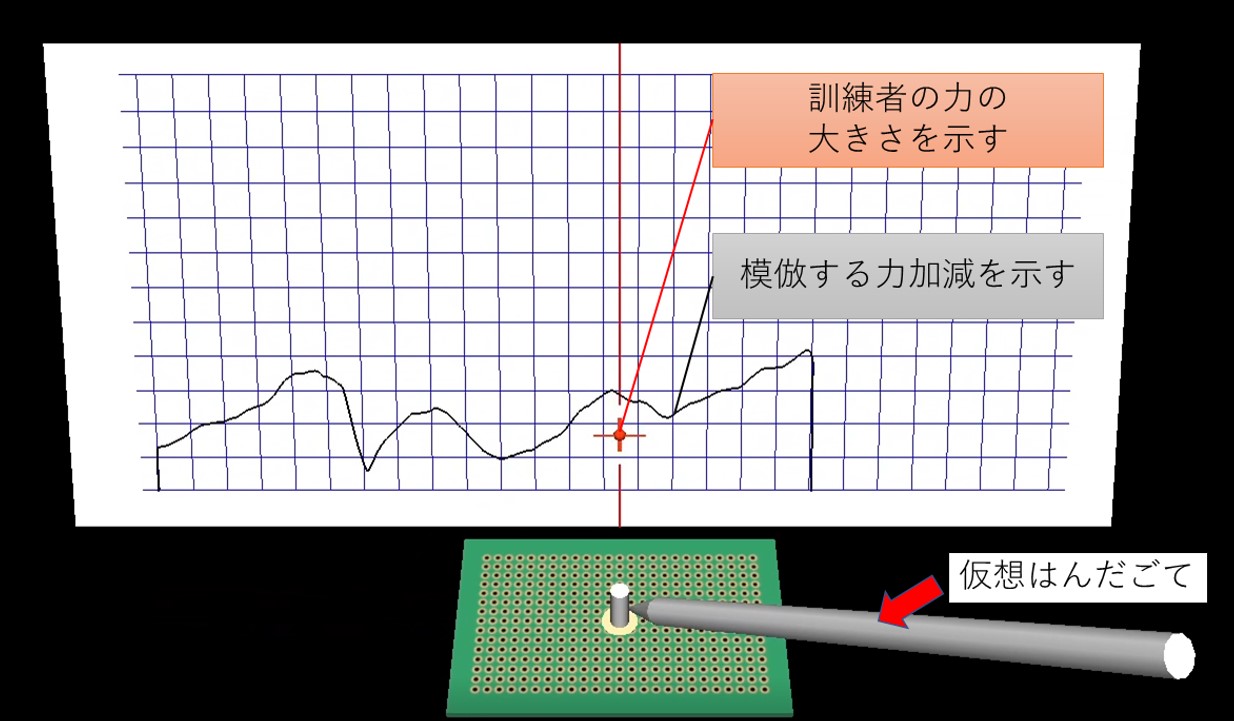
Training in soldering operations