Development and evaluation of MR remote indication system for probe manipulation in ultrasonography
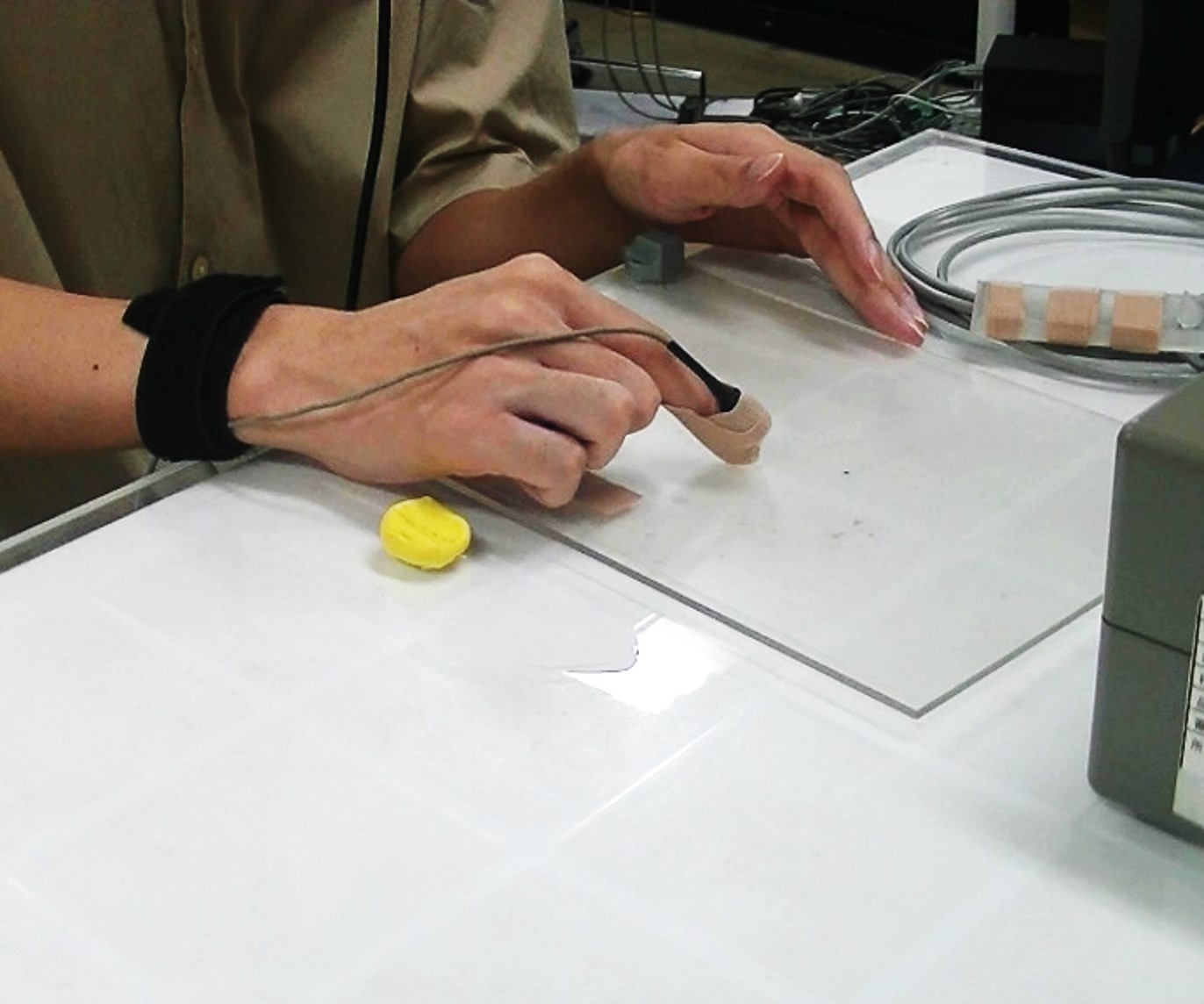
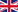
One form of telemedicine support is for a nurse to visit a patient's home and a physician to treat the patient remotely from a hospital. When ultrasonography is performed remotely, the physician gives verbal instructions to the nurse via videophone. However, the operation of the ultrasound probe in ultrasonography requires a high degree of expertise because the echo image produced differs depending on the position, angle, and strength of the probe. Therefore, it is difficult to give verbal instructions.
This study aims to develop a probe manipulation instruction system using mixed reality technology as an elemental technology for telemedicine, which enables nurses to perform ultrasound examinations while mimicking the movements of the ultrasound probe of a specialist doctor in a remote location.
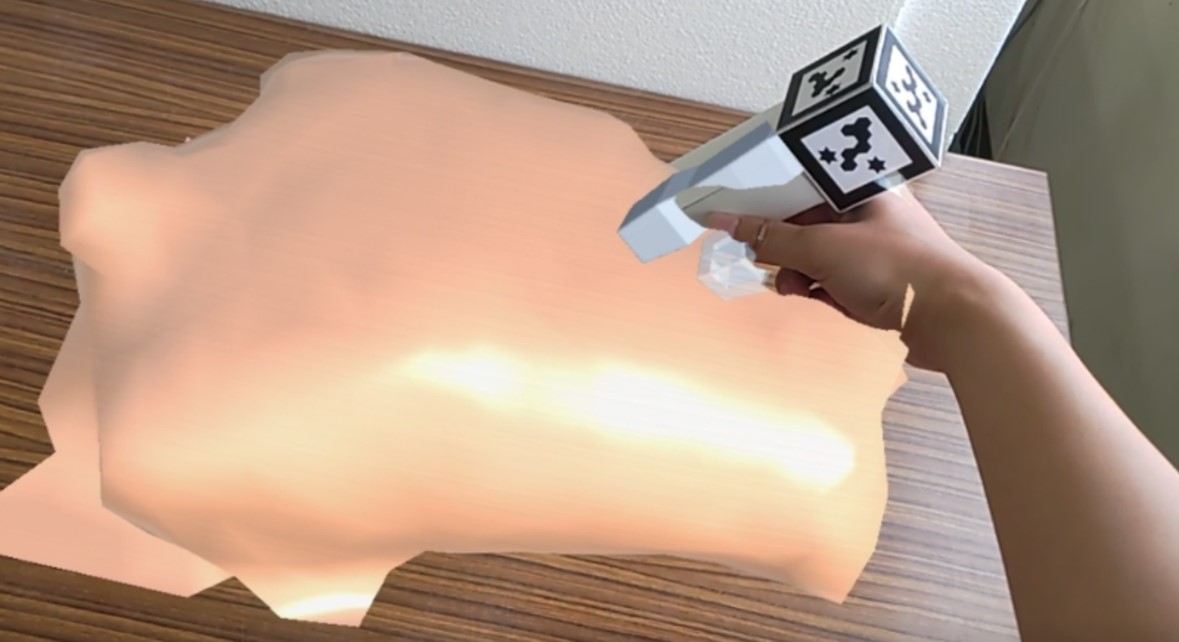


Evaluation of drawing function by finger on a board touched in VR space
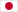
Recently, education using VR technology is expected to improve learning motivation and learning efficiency. We have developed a tangibles-based handwriting input system that enables users to draw letters and figures in VR space while actually touching an acrylic board in real space. In general touch panels, a change in the capacitance between the built-in electrodes occurs when the user touches the panel, and the system judges whether the user has touched the panel or not. On the other hand, this system uses a magnetic motion capture device to measure the position and posture of the acrylic board and fingers in real space, and judges the contact between the fingers and the acrylic board to realize drawing characters and figures on the board in VR space.
In this study, we will conduct a comparison experiment by tracing Chinese characters on a real-space touch panel and a board in VR space, and evaluate the ease of writing the character input function of the system we have constructed.